Brain Health: Nutrition Part 2
How is the gut linked to brain health?
We ended our previous blog by mentioning that your gut also plays an important role in your nutrition and brain health. So let's dive right into today's blog about how gut and brain health are related.
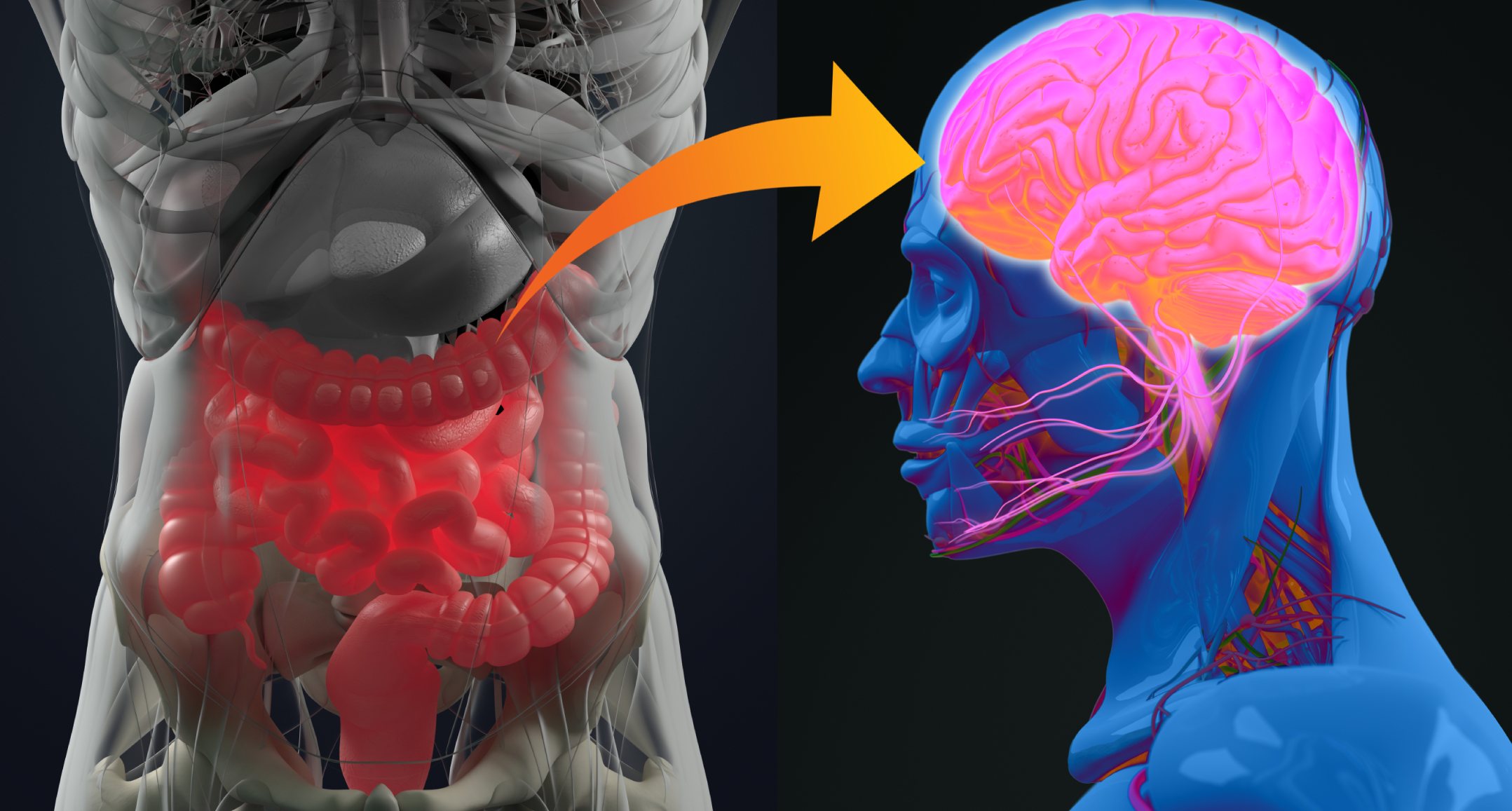
The gastrointestinal tract (GIT) is vital for the absorption of nutrients. However, important constituents of the GIT, the gut microbiome, also play multiple roles in maintaining a healthy brain. The gut microbiome refers to the vast number of bacteria in the gut. These bacteria aren't just hitching a free ride by using our body's nutrition to survive. Instead, research has shown that good bacteria in the gut have been playing vital roles in the human body. Various systems and neurons link the gut and the brain, creating the gut-brain axis. The gut-brain axis allows the brain to influence various intestinal activities and for the gut to influence cognitive functioning, mood, and mental well-being.
The gut microbiome can alter the nutrients available for absorption because they assist in the digestion of food, processing of nutrients, and the conversion of food into various compounds, such as neurotransmitters and metabolites. Metabolites produced by the gut microbiome play a role in modulating the immune system, exerting hormone-like activities, and interacting with various nerves. Furthermore, some metabolites can cross the blood-brain barrier and influence brain development, behaviour, and inflammation. Research has shown that disruptions in the composition of the gut microbiome called dysbiosis, may lead to symptoms of anxiety, depression, autism spectrum disorder, and Alzheimer's disease.
🧠Therefore, we need to follow a healthy diet to help strengthen the gut-brain axis and maintain a healthy balance of good bacteria in the gut so that we can keep our brains healthy. However, remember that the gut-brain axis works both ways, so a stressed, sleep-deprived and unhealthy brain may cause issues with your gut and trigger dysbiosis🧠
To maintain good gut bacteria eat healthy foods, limit or abstain from processed and unhealthy foods, consume enough fibre such as grains and beans, drink adequate amounts of water and take probiotics.
Previous research has suggested that consuming probiotics along with a healthy, balanced diet, is beneficial for healthy brain functioning. Apart from taking supplements to incorporate probiotics into your diet, what foods contain probiotics?🤔 Well, usually fermented foods contain probiotics such as:
- Yogurt
- Kombucha
- Pickles ( in salt, not vinegar)
- Cottage cheese
- Sourdough bread

Comments
Post a Comment